Pulse surveys in Banking & Financial Services: A 2026 guide for HR and risk leaders
Pulse surveys are short, frequent, and targeted questionnaires designed to measure real-time sentiment among employees or customers. Banks and financial institutions operate under constant regulatory scrutiny while managing aggressive growth targets and rising customer expectations.
This guide presents tested pulse survey frameworks used across financial institutions to monitor engagement, compliance culture, and burnout risk in real time. It outlines practical strategies that connect employee feedback with operational outcomes, helping HR and risk leaders implement structured listening programs that strengthen trust.
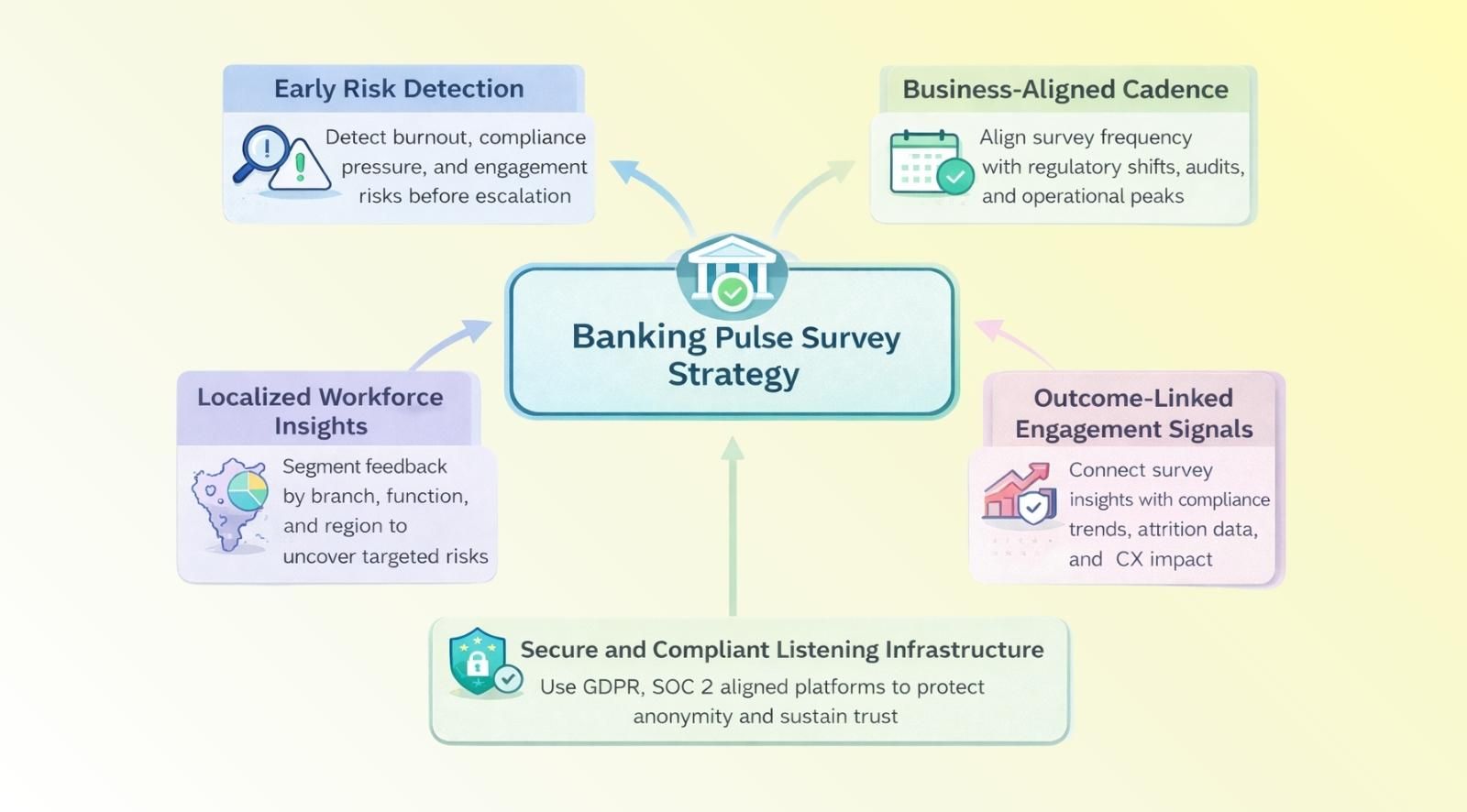
- Use pulse surveys to detect burnout, compliance pressure, and engagement risks early across banking teams.
- Align survey cadence with business pressure, regulatory change, and organizational transitions.
- Segment feedback by branch, function, and region to identify localized workforce risks.
- Link engagement signals with compliance, attrition, and customer experience outcomes.
- Use secure, compliant survey platforms to maintain anonymity and drive continuous employee listening.
Why pulse surveys matter more in banking than other industries?

Banking engagement risk directly affects compliance exposure, conduct risk, and customer outcomes, making workforce sentiment a governance issue rather than an HR metric. Pulse surveys give leadership continuous signals on pressure points that traditional annual surveys miss, enabling earlier intervention before burnout, ethical drift, or compliance breaches surface through audits or attrition spikes.
A pulse survey in banking is a short, recurring employee feedback mechanism used to monitor engagement, compliance culture, ethical climate, and frontline stress levels across financial institutions.
It enables leaders to detect conduct risks early, strengthen institutional trust, and align workforce sentiment with regulatory and operational stability requirements across distributed banking services.
- Continuous regulatory pressure from SOX, GDPR, and internal audit scrutiny
- High customer-facing pressure in retail and frontline banking roles
- Sales targets often create tension with compliance obligations
- Risk-averse culture discourages open feedback and escalation
- Burnout risks remain high in front-office and revenue-driving teams
- Hybrid operations create engagement gaps between branch and corporate employees
Unique engagement challenges in banking and finance
Engagement risks in financial institutions vary sharply by function, making uniform survey strategies ineffective. HR and risk leaders must interpret feedback through operational context, since stress drivers in revenue teams, compliance units, and support operations differ significantly and demand tailored listening and intervention approaches.
Pulse surveys must therefore segment engagement signals by business function, allowing leadership to identify localized pressure points before they evolve into conduct risks, attrition spikes, or performance decline.
- Retail banking: Branch employees face constant customer interaction pressure while balancing aggressive sales expectations with strict compliance requirements.
- Investment banking: Long working hours, deal deadlines, and performance-linked compensation models drive sustained burnout risk and attrition.
- Risk & compliance teams: High accountability and constant regulatory scrutiny create mental stress and low tolerance for operational error.
- Back-office operations: Repetitive processes and volume-driven workloads often result in disengagement and process fatigue over time.
- Fintech and hybrid teams: Rapid growth, remote work models, and evolving roles create alignment and culture gaps across distributed teams.
How to design a pulse survey for banking institutions to get actionable insights
Pulse surveys in banking must balance engagement measurement with regulatory sensitivity, operational realities, and employee trust. Poorly designed surveys risk low participation, defensive responses, or compliance concerns.
Effective survey programs, therefore, focus on brevity, psychological safety, and actionable insights that leadership can tie to workforce stability, conduct risk, and performance outcomes.
Survey design should minimize response effort while maximizing clarity, ensuring frontline and control functions can provide honest feedback without fear of exposure or misuse of data.
Core survey design principles
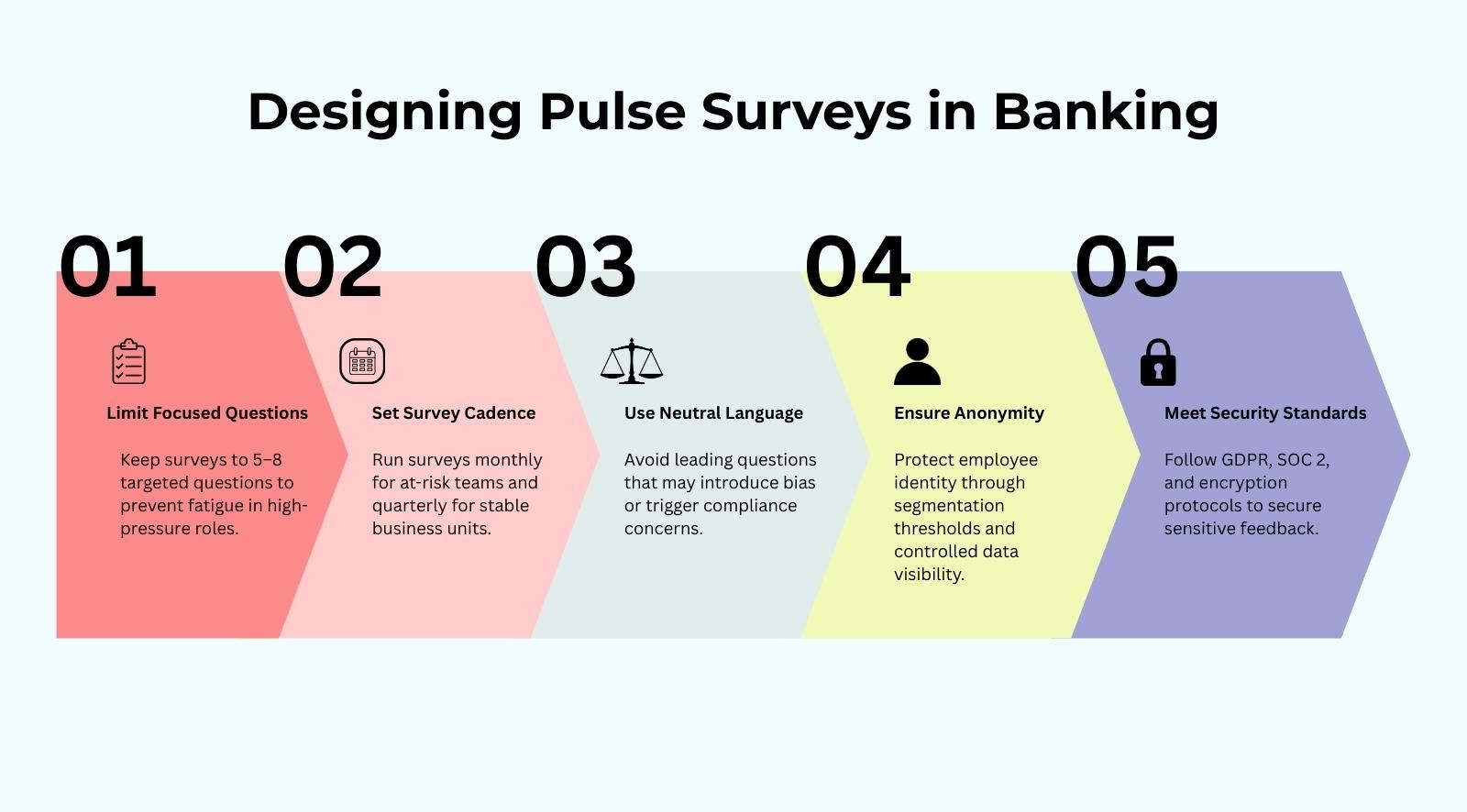
- Limit surveys to 5–8 focused questions to prevent fatigue in high-pressure banking roles
- Run surveys on a monthly cadence for high-stress functions or quarterly for stable divisions
- Maintain department-level anonymity thresholds to protect survey respondents' identity in smaller teams
- Use compliance-safe, neutral language that avoids blame or regulatory sensitivity
- Avoid leading or biased questions that influence employee responses
- Offer multilingual surveys, especially for EU and multinational branch networks
Security considerations
Security and data governance directly influence participation rates in banking surveys. Employees must trust that responses cannot be traced or misused, particularly in regulated environments.
Survey platforms must therefore demonstrate enterprise-grade data controls aligned with banking compliance standards.
- End-to-end data encryption during transmission and storage
- Full compliance with GDPR and regional data privacy regulations
- Independent security certification such as SOC 2 compliance
- Elimination of personally identifiable response tracking
- Clear data hosting options aligned to EU or US regulatory requirements
A secure survey framework reassures employees that feedback improves workplace conditions without creating personal or compliance risks.
Best pulse survey questions for banking employees

Effective banking pulse surveys use concise, behavior-focused questions that capture compliance culture, workload pressure, and leadership trust without survey fatigue.
Compliance & ethics
- I feel comfortable reporting unethical behavior without fear of retaliation.
- My team prioritizes compliance requirements over short-term business targets.
- Compliance expectations are clearly communicated in my role.
- I trust that ethical concerns are taken seriously by management.
Burnout & workload
- My workload is manageable within my working hours.
- I have adequate recovery time after peak workload periods.
- Work pressure does not regularly impact my personal well-being.
- Staffing levels in my team are sufficient to meet business demands.
Leadership & trust
- Senior leadership communicates business and regulatory changes transparently
- My manager supports the team during high-pressure situations.
- Leadership decisions reflect long-term stability over short-term gains.
- I trust leadership to act on employee feedback.
Customer & sales pressure
- Sales or revenue goals do not compromise ethical behavior in my team.
- Customer satisfaction can be managed without violating compliance standards.
- I do not feel pressured to meet targets in ways that create conduct or compliance risks.
How often should banks run pulse surveys?
Survey frequency in banking should align with operational risk, workforce pressure, and organizational change cycles rather than fixed HR calendars. Running surveys too infrequently delays risk detection, while excessive surveying reduces participation. Decision-makers should align cadence with business volatility and employee stress exposure.
Recommended survey timing triggers
- Run monthly surveys in high-pressure or revenue-driving teams where burnout and conduct risks rise quickly
- Use a quarterly cadence for stable operational or support divisions
- Launch surveys after major regulatory or policy changes impacting employee workflows
- Deploy surveys post-merger or acquisition to monitor integration and culture risks
- Use targeted pulses during restructuring or workforce transitions
Recommended survey cadence by situation
| Business situation | Recommended frequency | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Frontline sales or trading teams | Monthly | Detect burnout, conduct pressure, and attrition risks early |
| Stable back-office or support divisions | Quarterly | Track engagement trends without causing survey fatigue |
| Post-regulatory change rollout | Immediate + follow-up pulse | Measure adoption challenges and operational friction |
| Post-merger or acquisition integration | Monthly for first 6 months | Monitor culture alignment and transition risks |
| Organizational restructuring or layoffs | Monthly during transition | Detect morale decline and trust gaps early |
How to analyze pulse survey data in banking
Pulse survey analysis in banking must move beyond engagement scoring and focus on operational risk indicators, workforce stability, and conduct culture signals. The objective is not to produce reports but to detect pressure points that affect compliance outcomes, customer experience, and employee retention.
Effective analysis therefore combines organizational segmentation, trend tracking, and correlation with business performance metrics.
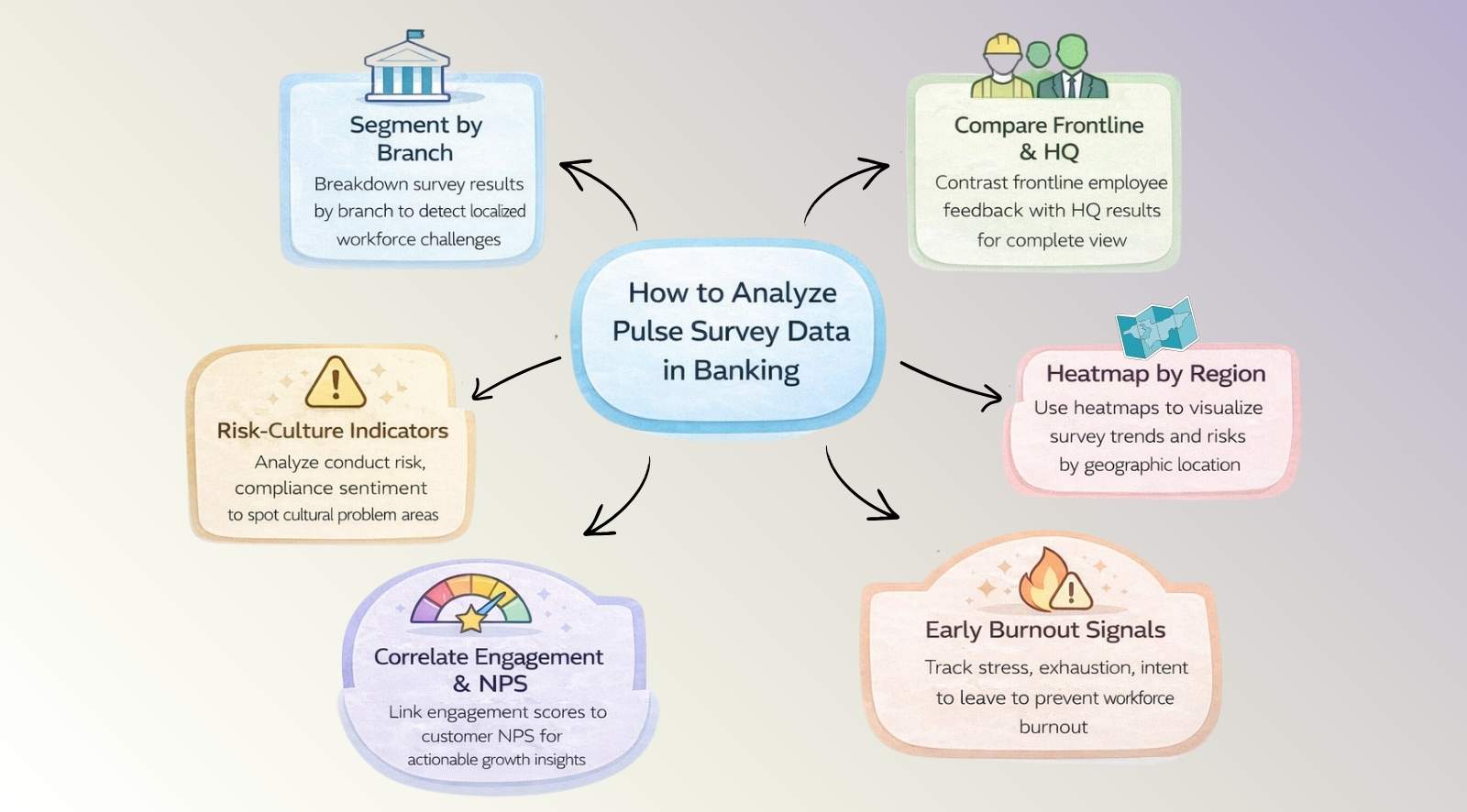
Segment results by branch and business unit
Segmenting survey data by branch, channel, product, or customer segment can reveal patterns that inform service improvements.
Branch-level analysis reveals localized engagement and compliance risks often hidden in organization-wide averages. Sales pressure, staffing shortages, or leadership quality frequently differ across locations, creating uneven employee experience and conduct exposure.
Leaders should:
- Compare engagement scores across branches of similar size or customer volume
- Identify locations showing consistent decline in trust, workload balance, or ethical comfort indicators
- Flag branches where engagement drops coincide with rising attrition or customer complaints
This enables targeted intervention instead of blanket engagement programs.
Compare frontline survey respondents with headquarters functions
Frontline banking roles experience customer conflict, sales pressure, and regulatory enforcement differently than headquarters teams. Aggregated data masks these differences.
Analysis should:
- Compare engagement and burnout indicators between customer-facing and corporate roles
- Track workload and ethical pressure signals within sales-driven teams
- Identify whether policy decisions at headquarters create unintended operational pressure at branch level
A widening engagement gap between frontline and HQ teams often predicts rising turnover or conduct risks.
Use regional heatmaps to detect systemic patterns
Regional heatmaps allow leadership to visualize engagement and risk signals across geographic markets. Economic conditions, regulatory enforcement intensity, or local leadership quality often influence employee sentiment.
Key uses include:
- Detecting regions with repeated workload or burnout signals
- Identifying clusters of low trust or compliance confidence
- Tracking improvement after leadership or operational interventions
Heatmaps support data-driven resource allocation rather than assumption-led decisions.
Track risk and compliance culture indicators
Banking pulse surveys must include signals linked to ethical conduct and compliance adherence. Monitoring these indicators prevents issues from surfacing only through audit failures or regulatory action.
Critical indicators include:
- Comfort in reporting unethical behavior
- Perceived pressure to bypass compliance for business goals
- Trust that misconduct is handled fairly
Declining scores often precede whistleblower complaints or compliance breaches.
Detect early-warning burnout signals
Burnout rarely appears suddenly. Survey trends usually show gradual deterioration in workload, recovery time, and leadership support metrics.
Early-warning analysis includes:
- Tracking sustained workload complaints across multiple cycles
- Monitoring recovery time or staffing adequacy scores
- Identifying teams where burnout indicators coincide with rising sick leave or attrition
Early intervention reduces replacement costs and stabilizes team performance.
Correlate engagement with customer and business outcomes
Advanced analysis links employee feedback with operational metrics. Banks increasingly correlate engagement with customer overall satisfaction and performance indicators.
Recommended correlations include:
- Engagement vs customer NPS at the branch level
- Burnout scores vs service quality error rates or complaints
- Leadership trust vs voluntary turnover trends
When engagement drops and customer satisfaction worsens together, the need for workforce intervention becomes clear.
Effective pulse survey analysis therefore shifts engagement programs from HR reporting exercises to enterprise risk and performance management tools.
Common pitfalls banks should avoid when running pulse surveys

Pulse surveys fail in banking when leadership treats them as engagement exercises rather than risk intelligence tools. Poor execution erodes employee trust, suppresses honest feedback, and eliminates early-warning signals needed to prevent conduct and compliance failures.
Avoiding common implementation mistakes is therefore critical for protecting institutional reputation and workforce stability.
Ignoring psychological safety in feedback collection
Employees will not provide honest responses if surveys are perceived as traceable or punitive. In banking environments where mistakes carry career consequences, fear of exposure directly suppresses reporting of ethical or operational concerns.
Leaders must ensure:
- Strict anonymity thresholds for small teams
- Clear communication that feedback is non-retaliatory
- Visible action on survey outcomes
Without psychological safety, targeted surveys generate compliance-safe but operationally useless data.
Weak ethical reporting culture integration
Pulse surveys often run parallel to whistleblowing or ethics programs without integration. When feedback mechanisms operate in silos, early conduct signals remain unaddressed.
Banks should:
- Align pulse survey questions with conduct and ethics reporting frameworks
- Track employee comfort in raising ethical concerns
- Connect engagement insights with internal audit and compliance monitoring
Integrated feedback ecosystems strengthen ethical reporting and gives deeper understanding of culture before issues escalate.
Misinterpreting conduct risk indicators
Organizations frequently overlook engagement data linked to conduct risks. Pressure to meet targets, workload imbalance, or distrust in leadership often precede ethical lapses.
Critical warning signs include:
- Employees reporting pressure to bypass compliance
- Falling trust in leadership decisions
- Rising burnout within revenue-driving functions
Ignoring these signals allows conduct risks to mature into regulatory or reputational incidents.
Failing to detect misconduct early
Many institutions act only after formal complaints or audit findings surface. By that stage, damage is already done. Pulse surveys can reveal misconduct risks earlier if analyzed correctly.
Effective programs:
- Track declining ethical comfort trends across survey cycles
- Monitor teams reporting pressure to compromise standards
- Escalate recurring risk signals to leadership before incidents occur
Early detection reduces legal, regulatory, and reputational exposure.
Treating surveys as HR exercises rather than compliance safeguards
A common failure occurs when survey ownership remains isolated within HR without executive or risk leadership involvement. Engagement data then lacks operational consequence.
Successful banks:
- Treat survey insights as enterprise risk indicators
- Link findings to compliance, conduct, and operational reviews
- Hold leaders accountable for addressing workforce risk signals
Pulse surveys deliver value only when leadership converts feedback into preventive action that protects both employees and institutional integrity.
How CultureMonkey helps build a continuous employee listening culture in banking?
Technology and digitization are crucial for enhancing efficiencies in banking operations. Banks require listening platforms that balance engagement measurement with enterprise security, regulatory compliance, and scalable deployment across distributed teams.
CultureMonkey supports continuous listening by combining secure survey infrastructure with operational tools that enable HR and business leaders to translate feedback into measurable action without increasing administrative complexity.
The platform is positioned for institutions that require structured, compliant, and scalable employee listening rather than standalone survey execution.
Key capabilities relevant for banking institutions include:
- Enterprise-grade security with data encryption, GDPR alignment, SOC2 compliance, secure authentication, and controlled access frameworks suited for regulated environments
- 50+ research-backed survey templates supporting engagement, lifecycle, and pulse programs while allowing customization for banking-specific contexts
- Benchmark and trend analytics enabling leaders to compare engagement signals across teams and track historical patterns over time
- Role-based access controls allow HR, compliance, and leadership teams to view insights relevant to their responsibilities while protecting employee anonymity
- Multilingual and mobile-friendly surveys supporting distributed branch and global banking workforces across regions and languages
- Audit-ready reporting and historical data tracking helping organizations maintain visibility into engagement and risk trends across survey cycles
- API and HRIS integrations enabling seamless employee data synchronization with HR systems for easier survey deployment and organizational mapping
CultureMonkey is suited for banks seeking a continuous listening system that integrates securely into existing HR and compliance ecosystems while supporting data-driven workforce decisions without operational disruption.
.webp)
Run effective pulse surveys across your banking workforce
- Banking pulse survey templates
- Secure anonymous feedback
- Real-time engagement insights
- Enterprise Grade Security
Conclusion
Pulse surveys in banking succeed when they move beyond engagement measurement and become part of enterprise risk and workforce decision-making. Banking institutions that continuously monitor burnout signals, compliance culture, and frontline pressure are better positioned to prevent conduct failures, stabilize teams, and protect customer experience.
The priority for HR and risk leaders is not survey frequency but disciplined execution, secure data handling, and consistent action on feedback insights. Platforms that combine secure survey delivery, actionable analytics, and scalable deployment make this transition easier.
Solutions such as CultureMonkey support banks in building structured, continuous listening programs that align employee feedback with operational stability while maintaining the governance standards expected in the regulated financial sector.
Book a demo with CultureMonkey.
FAQs
1. What is a pulse survey in banking?
A pulse survey in banking is a short, recurring employee feedback survey used to monitor engagement, compliance culture, ethical climate, and burnout risks across branches and business units, enabling leadership to detect workforce issues and address risks early.
2. How do banks ensure anonymity in surveys?
Banks ensure anonymity by using department-level reporting thresholds, encrypted data collection, and platforms that remove personally identifiable information, ensuring employee responses cannot be traced while still providing actionable insights for leadership.
3. Are pulse surveys compliant with financial regulations?
Pulse surveys are compliant when platforms meet GDPR and data privacy standards, use encrypted data handling, and avoid collecting personally identifiable responses. Surveys must use compliance-safe language and secure data hosting aligned with banking regulatory requirements.
4. How often should financial institutions survey employees?
High-pressure banking teams benefit from monthly pulse surveys, while stable functions can use quarterly surveys. Additional pulses are recommended after regulatory changes, mergers, or restructuring to detect workforce stress and engagement risks early.
5. Can pulse surveys detect ethical risk?
Yes. Pulse surveys reveal early ethical risk signals by tracking employee comfort in reporting misconduct, pressure to bypass compliance, and trust in leadership decisions. Declining scores help banks detect conduct risks early and intervene before issues escalate into regulatory or reputational incidents.
6. What ROI can banks expect from pulse surveys?
Banks typically see ROI through reduced attrition, early burnout detection, improved compliance culture, and better customer experience. Continuous feedback allows leadership to intervene sooner, lowering replacement costs, preventing conduct risks, and stabilizing frontline performance across branches and business units.
7. How are pulse surveys different from annual engagement surveys in banks?
Annual surveys provide a broad culture snapshot, while pulse surveys deliver frequent, targeted feedback on workload, compliance pressure, and engagement risks. In banking, pulses help leadership detect emerging workforce and conduct issues earlier instead of waiting for yearly review cycles.
8. Who should own pulse surveys in banks, HR, Risk, or Compliance teams?
Ownership should be shared. HR manages survey execution and engagement action plans, while Risk and Compliance teams review insights linked to conduct and regulatory exposure. Joint ownership ensures employee feedback informs both workforce strategy and institutional risk management.
9. Can pulse surveys reduce employee attrition in banks?
Yes. Pulse surveys identify burnout, workload imbalance, and leadership trust issues early, allowing banks to intervene before employees resign. Continuous feedback helps stabilize frontline teams, improve manager responsiveness, and reduce replacement costs linked to voluntary turnover.












